The Endocrine System Anatomy
Introduction
The endocrine system is the collection of ductless glands that produce hormones that regulate metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, sexual function, reproduction, sleep, and mood.
The term “endocrine” comes from Greek, endo- ‘within’ + krinein ‘sift’, that means that the secretion produced by the gland is secreted inside the gland and then diffused to the capillaries that surround the gland to be distributed via circulation throughout the body where it will reach its target cell.
Learning Objectives
- To identify the major endocrine glands using an anatomical model or diagram.
- Pituitary gland; anterior and posterior pituitary glands
- Thyroid and parathyroid glands
- Adrenal gland
- Pancreas
- Testes
- Ovaries
- Identify major endocrine glands and its components at the microscopic level
- Pituitary gland – distinguish between the anterior and posterior lobes
- Thyroid – Identify the thyroid follicles, colloid and parafollicular cells
- Adrenal Glands – Identify the zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, zona reticularis, and adrenal medulla
- Pancreas – Identify pancreatic islets and acinar tissue
- To list the hormones secreted by each endocrine gland identified, and discuss the actions of each hormone identified
- Describe the nature of feedback loops that regulate the activity of the hypothalamus, pituitary and other endocrine glands
Before the lab
- Read “The Endocrine System” chapter from your textbook
- View assigned videos and animations
- Complete the pre-lab activities assigned by your instructor
Laboratory Activities
Gross and Microscopic Anatomy of the Endocrine System
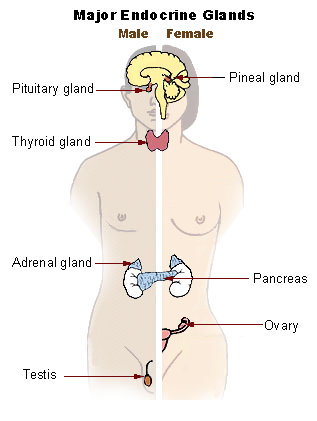
- Identify the major endocrine organs. Use anatomical models available in the lab and Figure 1 as reference.Use the table shown below and the space provided for drawings to complete this activity.
| Identify the following organs using: | Identified |
| A. Anatomical Models | |
| Hypothalamus | |
| Infundibulum | |
| Pituitary gland (Hypophysis) | |
| Anterior Pituitary – Pars distalis (Adenohypophysis) | |
| Posterior Pituitary – Pars nervosa (Neurohypophysis) | |
| Pineal gland | |
| Thyroid Gland | |
| Isthmus | |
| Right and left lobes | |
| Parathyroid glands | |
| Oxyphil and chief cells (if visible) | |
| Thymus Gland | |
| Pancreas | |
| Head | |
| Neck | |
| Body | |
| Tail | |
| Adrenal Gland | |
| Capsule | |
| Cortex | |
| Medulla | |
| Ovaries | |
| Testes |
- Identify the microscopic components of major endocrine glands. Use microscope slides available in the lab to complete this activity. Draw each of them.
| B. Microscope slides | Identified |
| Thyroid gland | |
| Follicles | |
| Follicular cells | |
| Colloid | |
| Parafollicular cells | |
| Adrenal gland | |
| Capsule | |
| Zona glomerulosa | |
| Zona fasciculata | |
| Zona reticularis | |
| Medulla | |
| Pancreas | |
| Acinar cells | |
| Islets of Langerhans | |
| Pancreatic ducts | |
| Ovaries | |
| *distinguish between oocytes and follicles | |
| Primordial follicles | |
| Primary follicles | |
| Secondary follicles | |
| 3rtiary, Vesicular or Graafian follicle | |
| Antrum | |
| Ovum | |
| Corpus Luteum | |
| Corpus Albicans | |
| Medulla and cortex | |
| Testis | |
| Seminiferous tubule | |
| Interstitial cell (Leydig cell) |
- Obtain prepared microscope slides of the major endocrine glands. Place the slides on the microscope stage, scan the slide using the scanning objective, once you have located the sample increase the magnification by using the low power objective to view the sample. Then use the high-power objective to see the cells associated with each of the endocrine glands and draw them in the space provided.
- Pituitary gland – make sure to label the anterior and posterior lobe
Total Magnification: - Thyroid – make sure to label the thyroid follicles, colloid and parafollicular cells

Total Magnification: - Adrenal Glands – Identify the zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, zona reticularis, and adrenal medulla

Total Magnification: - Pancreas – Identify pancreatic islets and acinar tissue

Total Magnification:
- Pituitary gland – make sure to label the anterior and posterior lobe
- List the hormones secreted by each endocrine gland identified, and discuss the actions of each hormone identified
Table 2: Hormones and their actions
| Organ | Hormones Secreted | Action of Hormones |
| Pineal Gland | Melatonin | |
| Anterior Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) | Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) | |
| Luteinizing hormone (LH) | ||
| thyroid-stimulating hormone (thyrotropin) (TSH) | ||
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) | ||
| Prolactin (PRL) | ||
| Growth Hormone (GH) | ||
| Posterior Pituitary Gland (Neurohypophysis) | Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) | |
| Oxytocin | ||
| Thyroid Gland (Colloid) | Triiodothyronine (T3) | |
| Thyroxine (T4) | ||
| Calcitonin | ||
| Parathyroid Gland | Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) | |
| Thymus | Thymosin | |
| Pancreas | Insulin | |
| Glucagon | ||
| Somatostatin | ||
| Adrenal Gland (cortex) | Corticosteroid Hormones | |
| zona glomerulosa | Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) | |
| zona fasciculata | Glucocorticoids (cortisol/hydrocortisone) | |
| zona reticularis | Gonadocorticoids (Androstenedione and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)) | |
| Adrenal Gland (Medulla) | Epinephrine and Norepinephrine | |
| Testes | Testosterone and Inhibin | |
| Ovaries | Estrogen, Progesterone and Inhibin |
- Describe the nature of feedback loops that regulate the activity of the hypothalamus, pituitary and other endocrine gland.

Additional Questions
You should also be able to answer the following questions:
- What is the general name for the types of organs that produce hormones?
- What name is given to cells or tissues receptive to hormones?
- Melatonin is secreted by which gland?
- Where is ADH stored?
- What is the effect of TSH, and where is it produced?
- What connects the two lobes of the thyroid gland?
- Does parathormone increase or decrease calcium levels in the blood?
- What does glucagon do as a hormone, and where is it produced?
- Which hormones in the adrenal gland control water and electrolyte balance?
- Which is the primary gland that secretes epinephrine?
- Where is growth hormone produced?
- What is another name for T3?
- Interstitial cells of the testis produce which hormone?
- What structures are responsible for the production of estrogen?
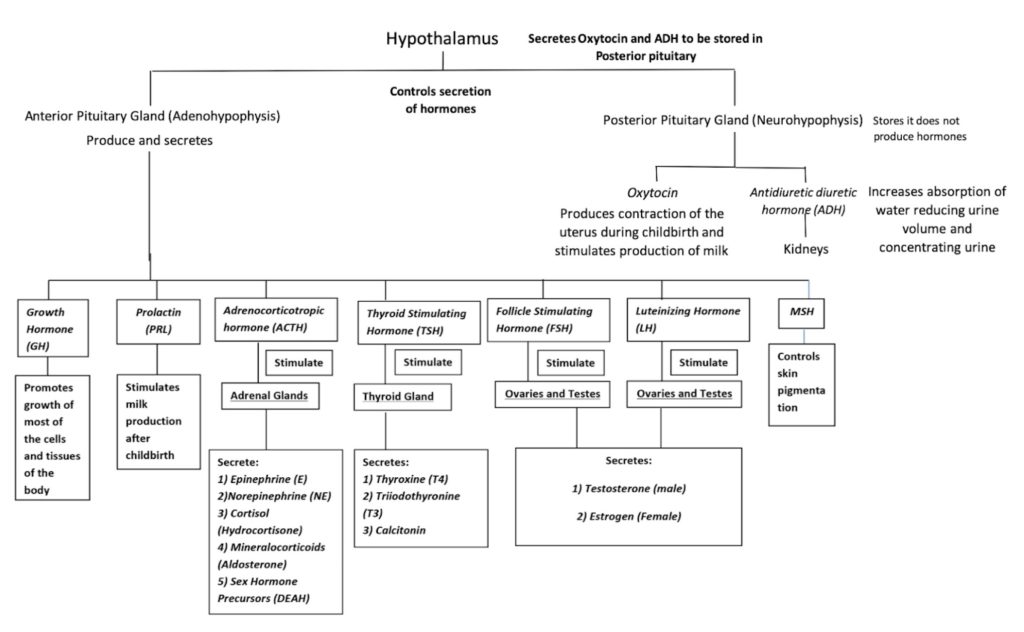
Appendix 1 – Hormone Flow Chart
Media Attributions
- Major Endocrine glands © Study is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Blank circle
- Hormone Flow Chart © Maria Carles is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license

