Chapter Five: Prenatal Development and Birth
Pregnancy Concerns
How long does a typical pregnancy last? People generally answer nine months, but that is not exactly true. Fetal life begins with ovum fertilization. Pregnancy is calculated from the first day of the woman’s last menstrual period and generally lasts about 40 weeks, which is closer to ten months!
Some early signs and symptoms of pregnancy are missed menstrual period, breast changes, aching in lower abdomen, fatigue, nausea and frequent urination.
During the first trimester women feel extreme fatigue, nausea and emotional changes. During the second trimester they begin to feel less nauseous, and the uterus expands into the abdominal cavity. During the third trimester, women anticipate the end of pregnancy and the uterus expands to the point below the breastbone.
From the first sign of pregnancy a woman needs to be careful about what she eats, drinks, and how she takes care of her body. Many factors can have an impact on the health and well-being of the embryo/fetus.
Risk Factors
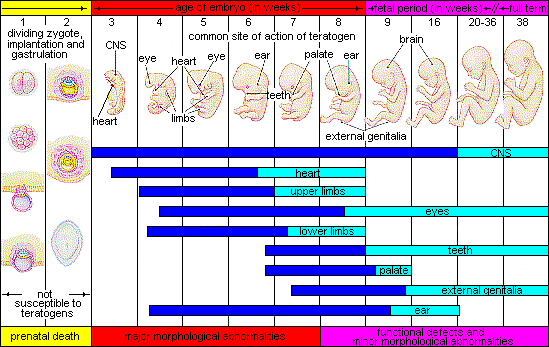
Teratogen
A teratogen is anything that causes a birth defect. The severity of the defect is determined by the dose, whether a child is genetically susceptible, and when they were exposed to the teratogen.
Antibiotics, some antidepressants, certain hormones, diet pills, aspirin and too much caffeine can all affect the fetus.
Psychoactive drugs act on the nervous system. They change moods and modify perceptions.
Alcohol can be extremely dangerous if it is abused when a woman is pregnant. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) causes cognitive and physical delays which can be extremely severe. FAS refers to a range of disorders caused by drinking alcohol during pregnancy. Fetal alcohol syndrome can cause abnormal facial features, growth deficiency, and problems with the central nervous system. Children with fetal alcohol syndrome may also have learning disabilities, attention span disorders, and other physical disabilities, including vision and hearing problems. The only way to prevent Fetal Alcohol Syndrome is to refrain from drinking during pregnancy.
Smoking during pregnancy can lead to low birth-weight infants who often struggle with lung development.
Cocaine, marijuana, methamphetamine and heroin are all teratogens that pose a great risk to the fetus.
Cocaine: Babies born to women who used cocaine often have smaller heads and a lower IQ. They struggle with cognitive performance, information processing, and attention to tasks.
Marijuana: Babies born to mothers who smoke marijuana have a lower birth weight and underdeveloped lungs.
Methamphetamine: Women who use methamphetamines are more likely to miscarry or give birth to low birth-weight infants. Infants experience irritability, feeding issues and failure to thrive.
Heroin: Babies born to women who used heroin often experience serious withdrawal symptoms and are extremely irritable. Long term they can experience cognitive delays and attention issues.
Environmental Hazards
Environmental hazards also pose a great risk to the fetus. Fathers’ exposure to lead and radiation, certain pesticides, petrochemicals, toxic waste, and manufactured chemicals are all cause for concern.
Medical Conditions
There are also many medical conditions that can pose a risk to the fetus. (CDC)
Rubella is very dangerous for a woman and her developing baby. Most Americans are now vaccinated against rubella (MMR vaccine) but if a woman contracts rubella during pregnancy, it can have an extremely negative impact on her infant including:
- Deafness
- Heart Defect
- Cataracts
- Intellectual Disabilities
- Liver and Spleen Damage
- Low Birth-weight
- Skin Rash
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease. It is especially important that women share their sexual history with their OB/GYN to help protect their unborn baby. If a woman has syphilis, she can give birth to a baby that has cognitive delays.
Genital Herpes is also a sexually transmitted disease. If a baby is born vaginally, the baby can be born blind or can tragically die during the birth process. If a baby is born by c-section, they will be absolutely fine.
AIDS is a sexually transmitted disease that can be passed from mother to child through blood, breast milk and the birth canal. If a mother is being treated for AIDS, chooses to deliver by c- section and bottle feeds, the child’s likelihood of contracting AIDS decreases dramatically (Santrock, 2013).
Other Concerns
Other parental factors that can affect a fetus are obesity, maternal nutrition, maternal age, paternal age, emotional states and stress and maternal hormone treatments.
On average, a woman gains 25 to 35 pounds during pregnancy. Pregnant women need to drink lots of water and increase protein, iron, vitamin D, calcium, phosphorous and magnesium.
Women should be careful about how much weight they gain. Maternal obesity can increase hypertension, diabetes, respiratory complications and infections.
It is fine to exercise during pregnancy. Women should exercise for shorter intervals and decrease intensity as pregnancy progresses.
Avoiding teratogens, eating healthy food, decreasing stress and participating in a frequent, low impact exercise routine can help ensure a healthy baby and an easier birth process.

