1 Health and Wellness

Chapter Objectives
At the end of this chapter, the student should be able to…
- define health.
- define wellness.
- distinguish between health and wellness.
- explain the dimensions of wellness.
- explain the difference between controllable and uncontrollable health factors.
- explain what “health disparities” means.
- define the phrase “social determinants of health.”
- identify the five categories that the social determinants of health can be broken into.
The Basics of Health And Wellness
In this chapter, we will be addressing health and wellness.
Consider how you use these terms. Do you use them interchangeably? Take a moment and write down (in your own words) how you would define each.
A brief Google search will reveal numerous definitions of “health.” As recently as 2013, the Oxford Dictionary defined health as “the state of being free from illness and injury” (Brüssow, 2013). When we look at health through this lens, one would think that the only criteria for health is the lack of illness and/or injury. An arguably better and more holistic definition of health is probably this one from the World Health Organization (WHO). The WHO defines health as “a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity (World Health Organization, n.d.)” Through this lens, wellness would appear to be a component of health. It appears that many sources, including the Oxford online dictionary, have adapted this or similar definitions of health.
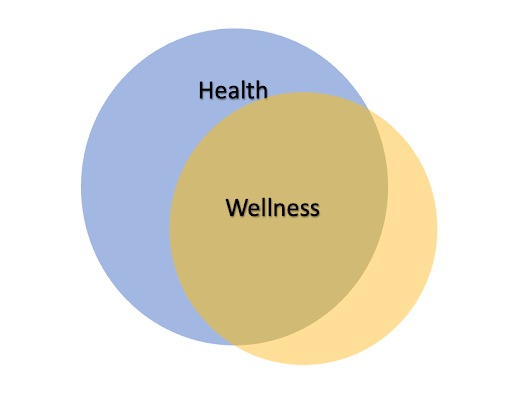
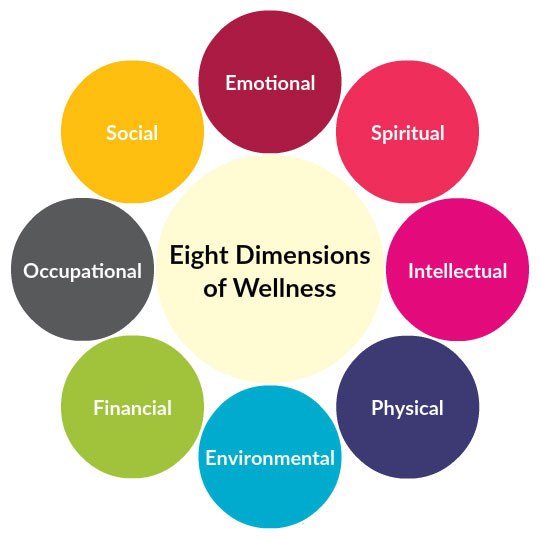
But what is wellness? Wellness is a holistic compilation of dimensions that enhance one’s quality of life and enable them to reach their full potential (Stoewen, 2015). While there are aspects of our health that we cannot control (more on this later on – see Health Factors), with wellness, we have some control over most aspects. Often, wellness influences our overall health. There are 8 dimensions of wellness, which include emotional wellness, physical wellness, occupational wellness, social wellness, spiritual wellness, intellectual wellness, environmental wellness, and financial wellness (Stoewen, 2015: 8 Dimensions of well-being).
Dimensions of Wellness
- Emotional Wellness – The ability to deal with stressors and the ups and downs of life in an effective and positive way (National Institutes of Health, n.d.).
- Physical Wellness – the ability to care for one’s physical body (Stoewen 2015). It includes physical activity, fitness, exercise, nutrition, substance use, and disease prevention (8 Dimensions of Well-being).
- Occupational Wellness– Wellness surrounding your satisfaction with your career or job (8 Dimensions of well-being). This dimension can be linked to financial wellness (see below), but there are some other considerations as well. Beyond the financial implications of your job or the career you have, your happiness and well-being are important. Consider things like job satisfaction, job safety, and work-life balance. Occupational wellness can also be called vocational wellness (Stoewen, 2015).
- Financial Wellness–The ability to live within your means, set goals, and plan for the future (Stoewen, 2015). There are two sides to financial wellness, including your income as well as the amount that you are spending. Just because one person makes more money than someone else does not mean they necessarily have a higher level of financial wellness, and vice versa.
- Intellectual Wellness is the desire and ability to learn and inquire (Stoewen, 2015). While traditional education is one way to achieve intellectual wellness, it is not the only way. Individuals with high intellectual wellness are lifelong learners (Stoewen, 2015). They are inquisitive, curious, and creative and use the resources available to them to expand their knowledge.
- Social Wellness– Social wellness is having good interpersonal relationships (Stoewen, 2015). It has more to do with the quality of relationships than the quantity of them. Someone with a high level of social wellness will have positive relationships with friends, family members, and significant others. They will be able to depend on their social group when needed and be available for others when those others are in need.
- Spiritual Wellness—Spiritual wellness is believing in something that gives your life value and meaning (Stoewen, 2015). It can be related to religion, but it does not need to be.
- Environmental Wellness- Environmental wellness relates to the relationship one has with the environment around them and how it impacts health and well-being (Stoewen, 2015). You can look at this in a few different ways. One way relates to what your current environment provides, such as clean water and clean air, and another is how you care for your environment (for example: recycling).
Health Factors
Some factors that affect our health we can control, but there are others we cannot. For instance, we cannot control genetics, race and ethnicity, age, or sex. A genetic disorder is caused by an abnormality that exists in someone’s genetic material (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, n.d). Additionally, some ethnicities are at an increased risk for certain diseases. Our risk of getting certain diseases also differs based on our biological sex and our age. There are still other uncontrollable influences on our health. For example, sometimes we are unknowingly exposed to harmful things in our environment. These environmental elements might include unknown pollutants in the air we breathe or the water we drink. There are also random events that can influence health and are out of our control—for example, injury or disability caused by extreme weather or the behaviors of others.
But there are also many aspects of health that we can control. For instance, we can choose to be more physically active, eat a more balanced diet, abstain from illicit drug use, smoking, and alcohol consumption, practice safe sex, surround ourselves with people who support us emotionally, and utilize safe online practices.
Social Determinants Of Health
When addressing health factors, it is important to consider health disparities. This can be done by looking at the social determinants of health. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (n.d.) “Social determinants of health are the conditions in the environments where people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age that affect a wide range of health, functioning, and quality-of-life outcomes and risks.” The social determinants of health influence one’s health and wellness. Social determinants of health have been broken down into 5 domains, including healthcare access and quality, neighborhood and built environment, social and community context, economic stability, and education access and quality.
There are different ways the domains may influence health outcomes. Disparities within these domains can influence one’s exposure to various environments or situations that could impact health, level of vulnerability to certain health outcomes, and what the consequences of different conditions might be (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, n.d.).
![]() Before reading on, list the 5 domains of the social determinants of health, write down what you think each domain means, and how each of these 5 domains may influence someone’s health.
Before reading on, list the 5 domains of the social determinants of health, write down what you think each domain means, and how each of these 5 domains may influence someone’s health.
Health care access and quality – When thinking about healthcare access and quality, you can think about your ability to receive proper medical treatment in a timely manner (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, n.d.). You could look at this as related to your physical distance from a hospital in an emergency. Other factors that may influence health care include health insurance, financial means, and health literacy. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, (n.d.), defines health literacy from individual people as “the degree to which individuals have the ability to find, understand, and use information and services to inform health-related decisions and actions for themselves and others.” Organizational health literacy can also be “the degree to which organizations equitably enable individuals to find, understand, and use information and services to inform health-related decisions and actions for themselves and others (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, n.d.).”
Neighborhood and built environment– When considering the neighborhood or built environment someone lives in, we can consider how safe the area is where someone spends the majority of their time (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, n.d.). This can include where someone lives, works, plays, learns, worships, and more. From an activity point of view, is this a safe place to be active? Is there a high crime rate? Are there sidewalks or parks where people can walk, jog, or ride a bike? Is there crime in the area, making it unsafe to be outside? Additionally, we need to consider environmental exposures such as the air and water in the areas we spend our time. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, (n.d.), individuals with low income, as well as racial and ethnic minorities, have a greater likelihood of living in places that pose safety and health risks.
Social and community context – Our overall well-being, health, and safety can also be positively or negatively impacted by our families (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, n.d.). Individuals are influenced and affected in different ways by the choices, beliefs, and actions of their families. In addition to our families, we are impacted by other members of our communities in schools, places of worship, and beyond. Especially for children, adolescents, and young adults, having role models and a good support system can increase exposure to good, safe environments and decrease one’s vulnerability to dangerous or unhealthy behaviors.
Economic stability- Economic stability can influence one’s health when basic needs cannot be met (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, n.d.). Beyond basic needs, economic stability can influence the likelihood that one will attend regular doctor’s appointments and seek medical attention when necessary. Financial strain can additionally cause added stress that increases one’s risk of various health outcomes.
Education access and quality- A higher education level is typically linked to higher income and better health (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, n.d.). According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, (n.d.), Children who experience discrimination, have disabilities, or are from low-income households are more likely to struggle with math and reading and less likely to attend college or even graduate from high school. This is important to mention when discussing access to quality education, but there is also more to consider than just the relationship between education, income, and health. It is also important to consider how one’s literacy influences health outcomes. Specifically, health literacy and information literacy are important when considering accessing health information and appropriate healthcare.

For more information on the social determinants of health, refer to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, (n.d.) Healthy People 2023.
Practical Application/ Laboratory Activities
Complete the Wellness Assessment
Answer The Following Questions
- Of the eight dimensions of wellness, select 3-4 that you identified as your strongest based on your personal wellness assessment. Explain why you are strong in these areas.
- Of the eight dimensions of wellness, select 3-4 that you identified as “needing improvement” based on your personal wellness assessment. Explain why these areas are more of a challenge for you. Brainstorm what you can do to strengthen these areas.
Self-Reflection
According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (n.d.), social determinants of health are the conditions in the environments where people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age that affect a wide range of health, functioning, and quality-of-life outcomes and risks.” In Chapter 1, the five domains related to social determinants of health were discussed. Share a time or situation where you, someone you know, or someone you heard of (no names or identifying information) was negatively impacted from a health standpoint due to a factor that falls under one or more of these domains.
Chapter Overview
In chapter one, you learned about health and wellness. Health is, as defined by the World Health Organization, “a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity (World Health Organization, n.d.),” and wellness is a holistic compilation of interconnected dimensions that all lead to increased quality of life and overall well-being (Stoewen 2015). The eight dimensions of wellness include emotional wellness, physical wellness, occupational wellness, social wellness, spiritual wellness, intellectual wellness, environmental wellness, and financial wellness. There are health factors that we can control and others that we cannot control. Additionally, it is important to consider health disparities. This analysis of control of factors can be done by looking at the social determinants of health. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (n.d.), “Social determinants of health are the conditions in the environments where people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age that affect a wide range of health, functioning, and quality-of-life outcomes and risks.”
Key Terms / Phrases:
Media Attributions
- Live well tiles © Photo by Brett Jordan on Unsplash is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Health Wellness circles © Jessica Alsup is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Health Wellness circles overlap © Jessica Alsup is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Eight dimensions of wellness © Wikipedia is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Light bulb
- Social Determinants of Health © Healthy People 2030 is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
Health is “a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.” (World Health Organization, n.d.)
Wellness is a holistic compilation of dimensions that enhance one’s quality of life and enable them to reach their full potential (Stoewen, 2015).
There are 8 dimensions of wellness, which include emotional wellness, physical wellness, occupational wellness, social wellness, spiritual wellness, intellectual wellness, environmental wellness, and financial wellness (Stoewen, 2015: 8 Dimensions of well-being).
Factors that influence our health that we have control over.
Factors that influence our health that we do not have control over.
Healthy People 2030 defines a health disparity as “a particular type of health difference that is closely linked with social, economic, and/or environmental disadvantage”(U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, n.d.)
According to Healthy People 2030 “Social determinants of health are the conditions in the environments where people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age that affect a wide range of health, functioning, and quality-of-life outcomes and risks.” (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services n.d.)
Healthy People 2030 defines personal health literacy as “the degree to which individuals have the ability to find, understand, and use information and services to inform health-related decisions and actions for themselves and others.” (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, n.d.)

