The ribosome is the translation machinery
The ribosome catalyzes peptide bond formation. The ribosome is a large complex assembled from many different components, including ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and protein. The rRNAs are functional RNAs that are never translated into protein.
The ribosome has a large and small subunit. The ribosomal components are described in terms of Svedburg units (S). These are units that indirectly approximate size based on sedimentation during centrifugation. The units are not additive, because sedimentation depends on both the size and shape of a complex. So for example, in prokaryotes the large subunit is 50S, the small subunit is 30S, and the whole ribosome is 70S.
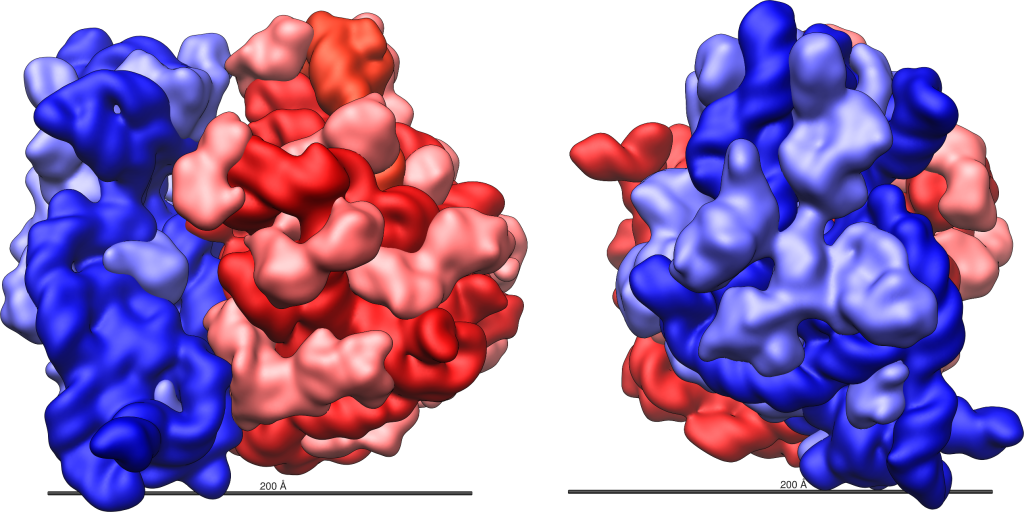
The structure of the E.coli ribosome is shown in Figure 6, with the large subunit colored red and the small subunit colored blue. Prokaryotic ribosomes have 3 ribosomal RNAs (rRNA): 23S rRNA and 5S rRNA in the large subunit, and 16S rRNA in the small subunit. They also have about 50 proteins.
Eukaryotic ribosomes also have a large and small subunit and are structurally very similar. In eukaryotes, the large subunit is 60S, the small subunit is 40S, and the whole ribosome is 80S. Eukaryotic ribosomes have 4 rRNAs and about 80 proteins. The 28S and 5.8S, and 5S rRNAs are part of the large subunit, and the 18S rRNA is part of the small subunit. It is the rRNA components that are catalytically active: they catalyze the peptidyl transferase reaction that builds the RNA molecule. The ribosome is therefore an example of a ribozyme, an RNA molecule that acts as an enzyme.
A comparison of the eukaryotic and prokaryotic ribosomes is summarized in Table 1.
| No Data |
Eukaryote Ribosome | Prokaryote Ribosome |
|---|---|---|
| Overall size | 80S | 70S |
| Large subunit | 60S | 50S |
| Large subunit components | 28S rRNA
5.8S rRNA 5S rRNA About 50 proteins |
23S rRNA
5S rRNA
About 30 proteins |
| Small subunit | 40S | 30S |
| Small subunit | 18S rRNA
About 30 proteins |
16S rRNA
About 20 proteins |

The large and small subunits assemble during translation with the mRNA sandwiched between them. The bases of the mRNA are being positioned within three adjacent sites in the ribosome, called the E, P, and A sites.
A stands for aminoacyl: this is the acceptor site for aminoacyl tRNAs (those carrying an amino acid) to enter the ribosome. P stands for peptidyl: this is the site of the peptidyl transferase reaction that forms peptide bonds between a growing polypeptide and an incoming amino acid. E stands for exit: tRNAs exit from the ribosome via the E site after they have donated their amino acid to the peptide.
Media Attributions
- Ribosome shape © Wikipedia is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- EPA sites © Amanda Simons is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license

